Micronutrients? Never Heard of it...

Contributed By: Amber Sullivan UGA Dietetic Student
What are micronutrients?
Micronutrient is a term that refers to vitamins and minerals. All micronutrients are not
produced by the body, and an adequate amount has to be consumed from the diet (CDC). The
only exception to this rule is Vitamin D, which the body can synthesize to some degree (CDC).
Vitamins and minerals are essential, and the body utilizes them to create enzymes, hormones,
and other substances needed for the maintenance and function of the body (WHO). Ultimately,
micronutrients are vital for healthy development, disease prevention, and the overall well-
being of an individual (CDC). If micronutrient consumption is insufficient, individuals may suffer
from micronutrient deficiency conditions. Examples of micronutrient deficiency conditions are
rickets and pellagra (CDC). Some cases may lead to death if not addressed in time (CDC).
However, it’s important to note that too many micronutrients may result in toxicity which can
be just as dangerous as micronutrient deficiencies.
So what foods should we eat to get all the nutrients we need? Short answer: eat a variety of
fruits and vegetables and you’ll be able to meet your nutrient needs. Want the long answer?
Check out the table below that lists vitamins and minerals and foods that they are commonly
found in. You’ll notice that foods provide more than just one nutrient.
Essential Micronutrients in Food
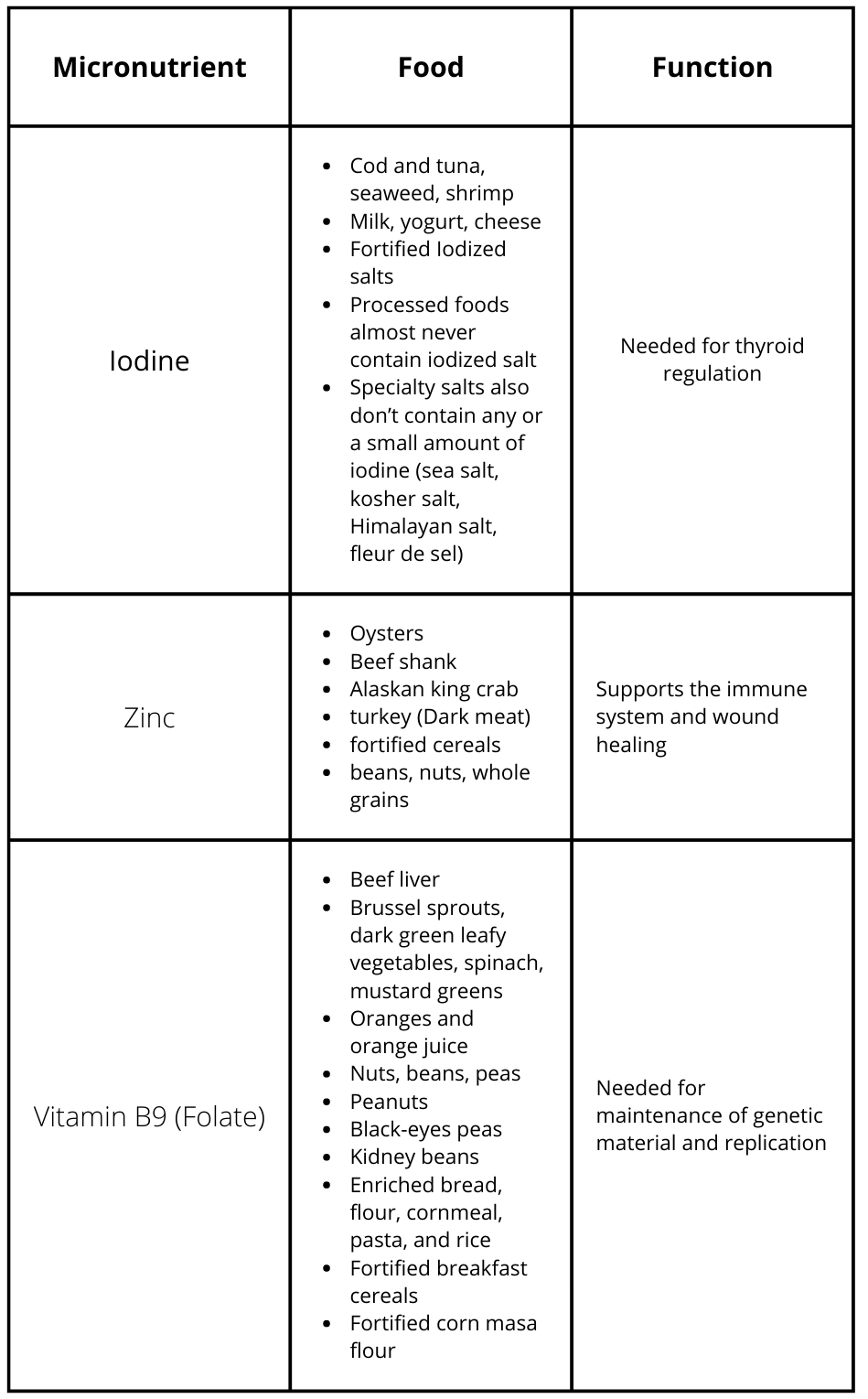
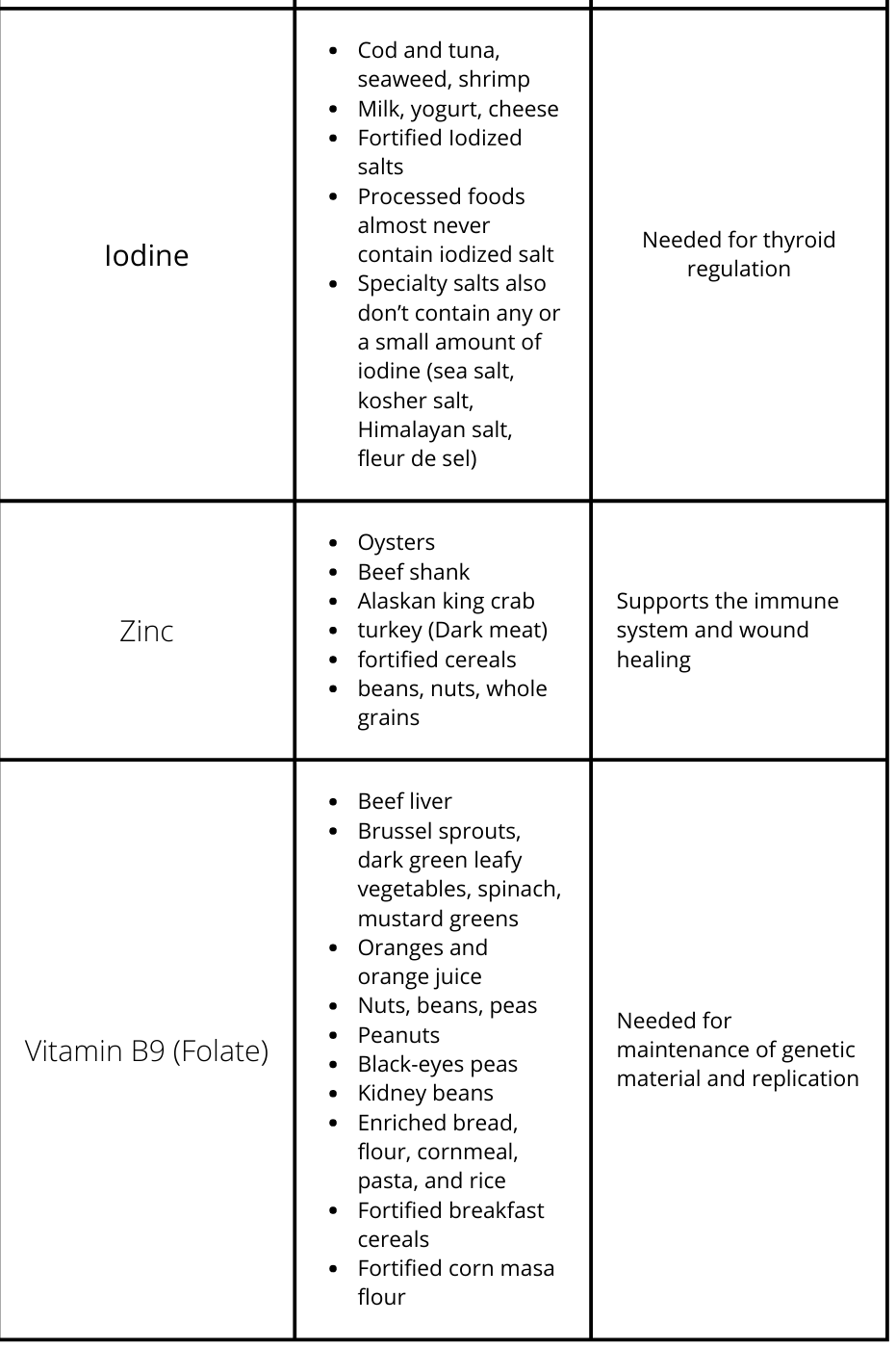
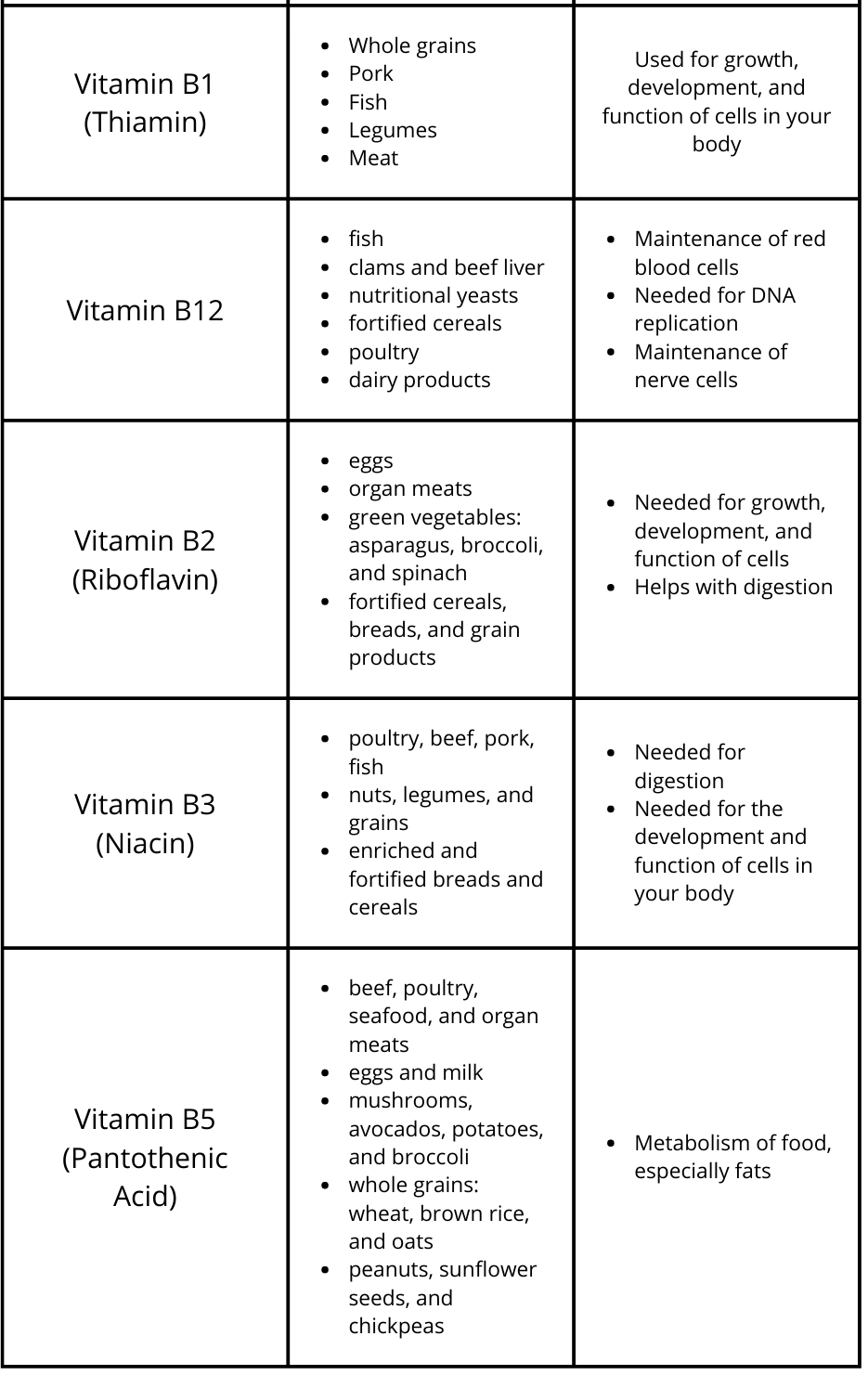
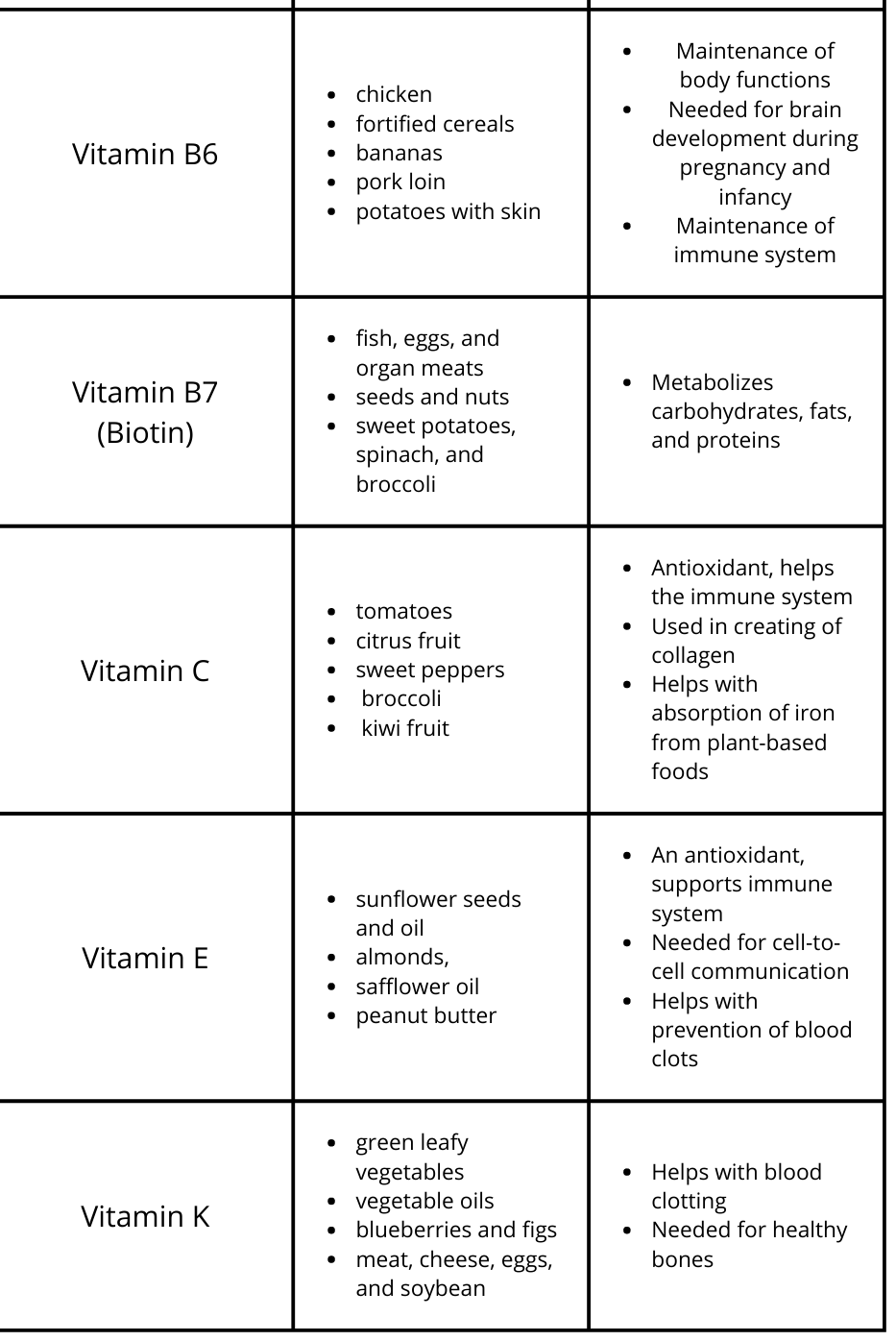
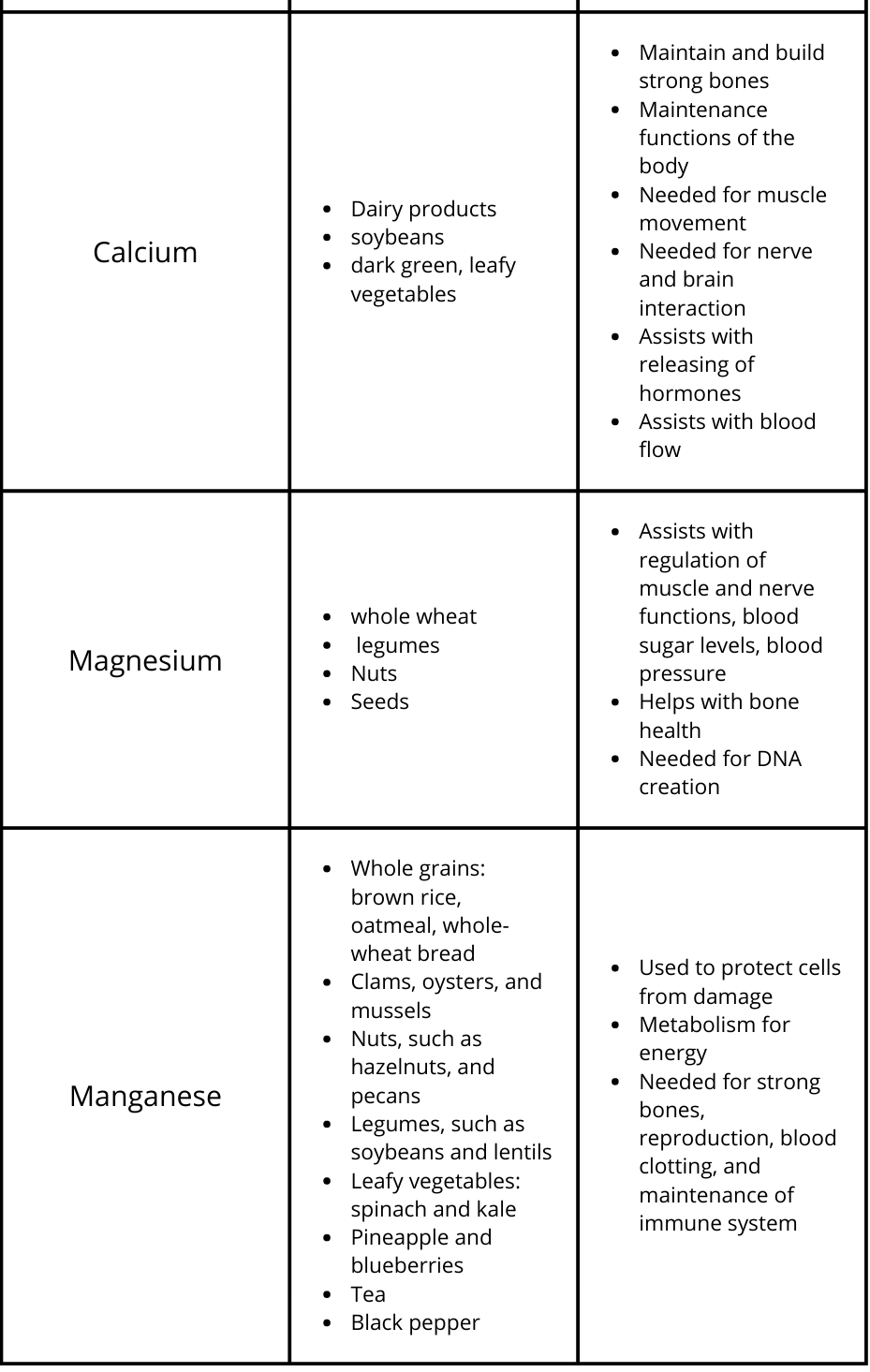
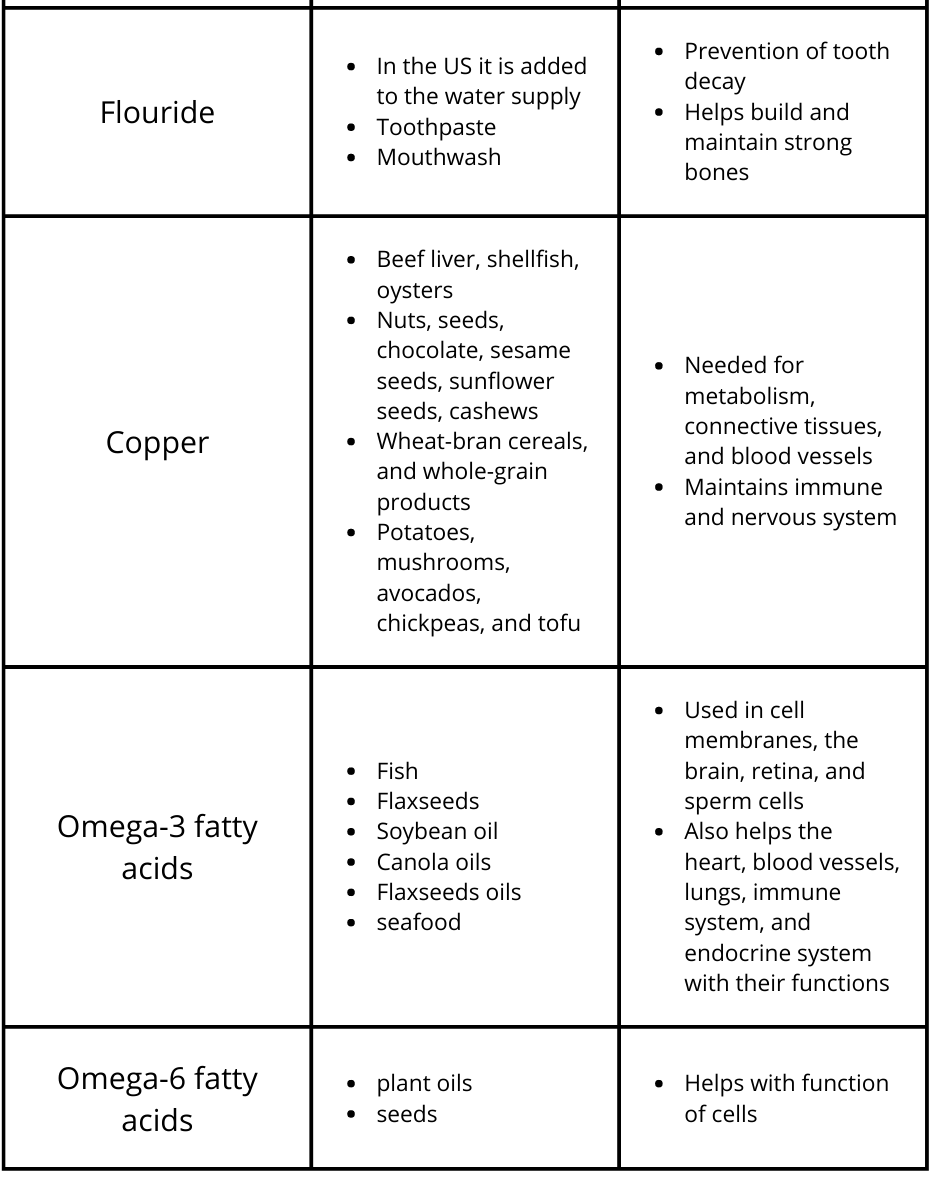
*Fortified means the vitamin or mineral in question was added to the product and is not normally found in the food at the amount listed on the nutrient label.
**Enriched means the nutrient in question was removed from the produce during processing but added back afterwards at the same amount or more than what was originally in the product
What if I don’t like or eat those foods?
If the foods listed above are not a part of your diet, supplements might be something to consider. (Check out the article on supplements here: link!). Taking a supplement can provide nutrients that you might be missing in your diet. However, you have to be careful with supplements because consuming too many vitamins and minerals can be harmful. Before starting a supplement, it’s best to talk to a medical professional so they can help you determine whether it’s safe for you to consume and the best way to go about it.
In conclusion, micronutrients are an essential part of the diet that allow your body to function at its best. The best way to get all of these nutrients is eating varied diet (think colorful fruits and veggies). Lastly, micronutrients are needed in small amounts, so take care when eating foods high in a specific nutrient, because too much can be dangerous!
Resources
Merz, B. (2021 February 15). Foods to boost your immune system and increase vitamin and mineral intake. Harvard Health Publishing: Harvard Medical School. https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/micronutrients-have-major-impact-on-health
CDC. (2022 February 1). Nutrition: Micronutrients Facts. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/nutrition/micronutrient-malnutrition/micronutrients/index.html
NIH. (2022 April 27). Dietary Supplement Fact Sheets. National Institute of Health: Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/list-all/
WHO. (2022 April 27). Micronutrients. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/health-topics/micronutrients#tab=tab_1
